BATTERY ROOMS
| 1. | The spark generating parts must have a distance to batteries of at least 0.5 m. This is valid for vented and valve regulated battery. |
| 2. | Hand lamps are only allowed without switches and protective glass. |
| 3. | The insulation resistance against earth is > 1 Mohm |
| 4. | Heaters with naked flame or glowing parts (glowing elements) are forbidden. |
| 5. | The battery room temperature should be between + 5° C and + 25° C. |
| 6. | Battery rooms have to be vented in a way that the gas (Hydrogen and Oxygen) evolved with charging and discharging is diluted so that explosions are impossible. |
| 7. | Earth connection of the racks or housings (i. e. cabinets) if they are made of metal. The earthing is not allowed if there is a protection insulation between the battery and the rack or cabinet. This insulation must withstand 4000 V for one minute. |
| 8. | Touch protection must be provided for all active parts at voltages > 60 V DC with insulation,covers or shrouds and distance. |
| 9. | Battery rooms must be dry and have to have a height of 2 m above the operating floors. |
| 10. | For vented batteries the floor surface must be electrolyte resistant. |
Battery Room Ventilation
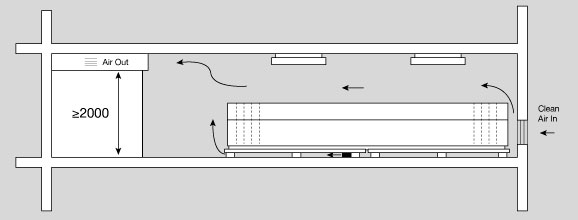
The way of air circulation should be as shown below.
If the air in and air out are on the same side the room free volume must be greater than 2.5 times of the calculated air volume.
| For calculation of the hourly to exchange air volume Q the following formula is valid: | |
| Q = 0.05 x n x I [m³/h] | |
| n = number of cells | |
| I = Value for the current from Table | |
| Calculation Example: | |
| Given: 220 V battery, 400 Ah, vented type, Antimony (Sb) < 3 % (LA) in FLOAT-service | |
| Q = 0.05 x n x I [m³/h] Ired = f1 x f2 x I | |
| Ired = reduced current (f1 and f2 see operating instruction of battery | |
| Q = 0.05 x 100 x 4 x 0.5 f1 = 0.5 if Sb in Pb is < 3 %, IU-charging up to 2.4 VPC | |
| f2 = 0.5 if the cell is valve regulated or a catalytic plug is used | |
| I = current (Table) in the example 1 A / 100 Ah | |
| n = number of cells, in the example 110 | |
| Q = 11 m3/h | |
| With natural ventilation (air convection) the minimum inlet and outlet area is calculated as follows: | |
| A ³ 28 x Q [cm²] | |
| (Air convection speed ³ 0.1 m/s) | |
| From this the minimum area for inlet and outlet to change hourly the calculated air volume of the example is: | |
| A = 28 x 11 m³/h = 308 cm² | |
| For mechanical ventilation the fan must be working during charging operation. If the charging is done above the gassing voltage of 2.4 VPC for lead acid batteries the fan must run at least for one hour after end of charging. | |
| If batteries are assembled in cabinets and used inside working areas it is required that the free air volume of the working area is ³ 2.5 times of the air volume Q. Otherwise a mechanical ventilation is required. | |
Battery Installation
| 1. | Batteries must be secured against dropping items and dirt. |
| 2. | It is necessary to have an insulation or a distance of at least 10mm for ³ 24 V potential difference to avoid parasitic currents. |
| 3. | The course width between battery rows is equal to 1.5 times the cell depth (replacement) but minimum ³ 500 mm. |
| 4. | The minimum distance for > 120 V between active parts is 1.5 m or insulation, insulated cover etc. |
| 5. | The distance to the wall for racks and cabinets is ³ 100 mm for a better placement of connections and better access for cleaning. |
| 6. | Batteries must be assessable easy that service with normal insulated tools can be made. |
